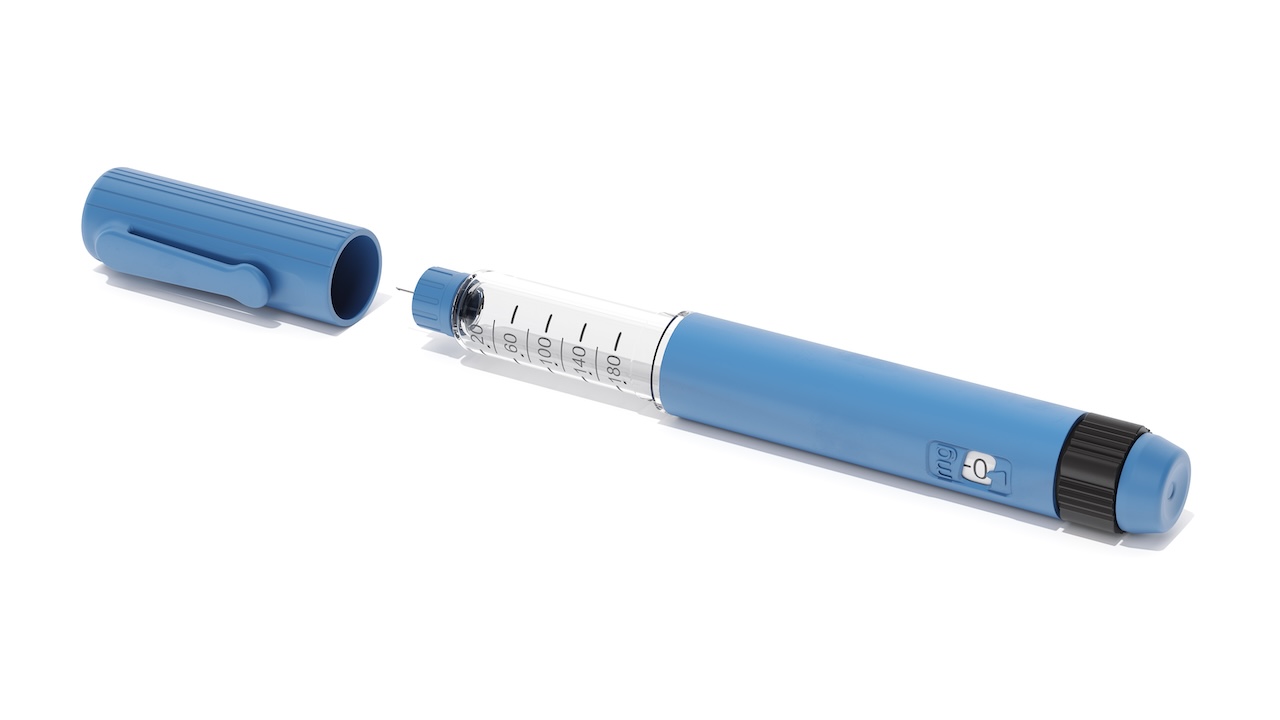
Innovations in micro injection molding
Engineering is about inventing solutions that can improve our lives, not only fixing existing problems. When it comes to the environment, the society and future sustainability, innovations in engineering has the potential to actually save the world from alerting issues including climate change, resource depletion, overpopulation, healthcare quality, pollution, waste disposal and water scarcity.
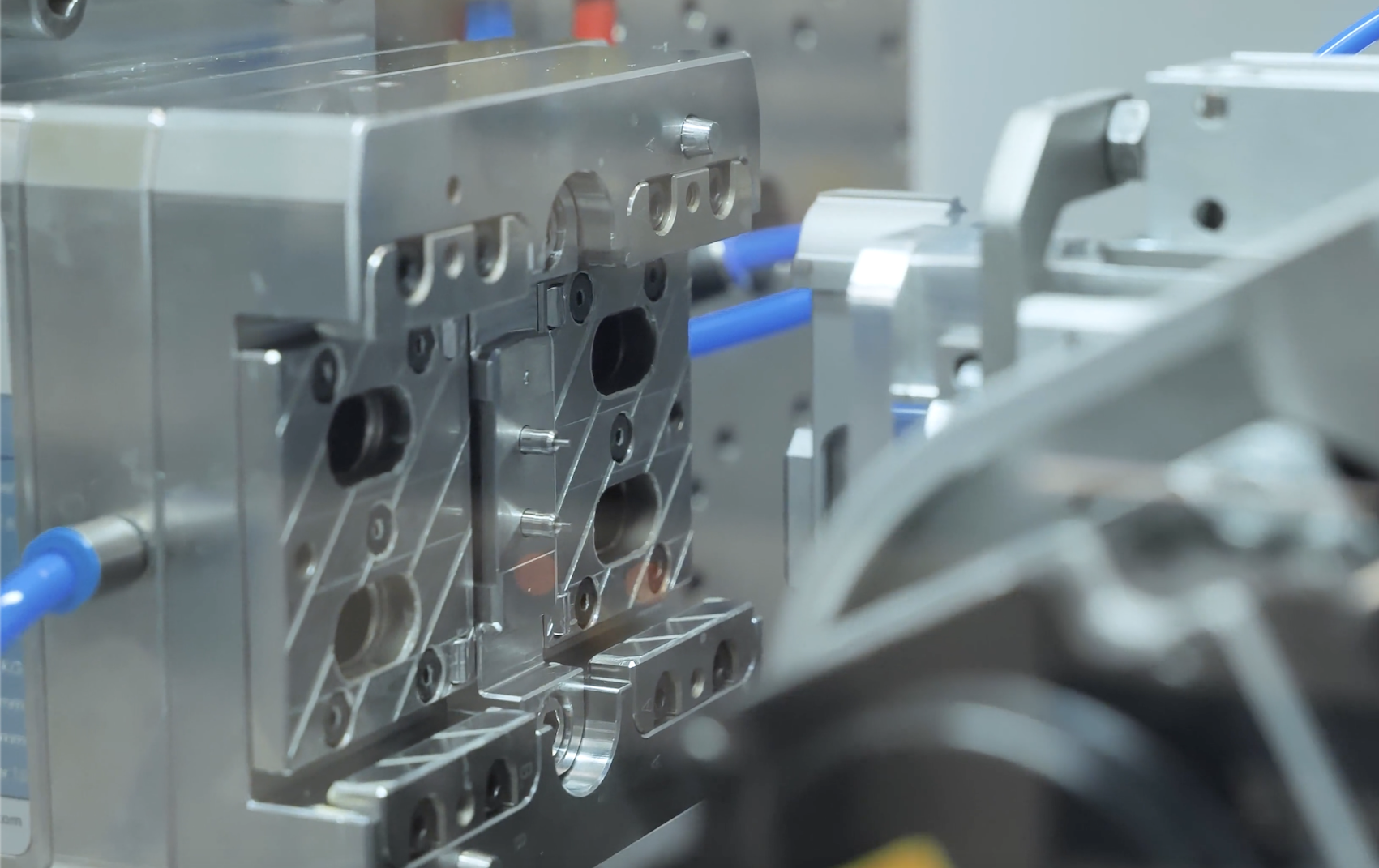

Innovation in micro molding helps manufacturers and customers reach new milestones every year (Photo: Micro Systems)
What is micro injection molding?
Micro injection molding is a highly specialised technique that involves CNC and EDM machined micro-structured steel or aluminium moulds to micron or even submicron scale tolerances, weighing a fraction of a gram or having tiny features varying from 50µm to 5µm or less.
When comparing micro injection molding and classic molding technologies, the shot size and injection machine accuracy are the main distinguishable features. As micro injection molding machines offer greater resolution feed choices, they can inject fractions of a gram with excellent precision, resulting in equal pressure distribution inside the cavity. Smaller molds are also utilized in micro injection molding. Precision CNC and EDM equipment are used to produce micro moulds with tiny cores, cavities and micro features on the interior.
Micro injection molding brings a number of benefits, including:
High quality: Micro injection molds are generally more precise than traditional moulds, resulting in superior surface finishes and fewer flaws on the final products. The technology can produce smaller features with tighter tolerances and, as a result, a smoother finish. The capacity to build microscopic features also implies that the quality of the final components will be better, as will the time it takes to make those parts.
Lower manufacturing costs: Micro injection molding could cost less than regular injection molding. Reduced clamping force, for example, necessitates smaller and less costly machinery. When compared to a full-priced tool, the cost of micro-injection molding is around 40% lower. Simultaneously, micro injection moulding uses shorter cycles than typical plastic injection moulding, which significantly reduces production costs. Compact barrels, fewer mould holes and small-sized runners are all important factors in lowering process costs. Also, most micro injection molding machines take less energy and time to create the same amount of pieces. As a result, if utilised properly, these devices can help save energy expenditures and maximise profits.
For example, with our experience in the design of conformal cooling channels in the mold inserts, cycle time reduction is highly achievable for our customers at Micro Systems. In a recent application, we have reduced cycle time from 6.5s to 3.5s, which significantly increases volume per machine cell and productivity.
Minimized plastic waste: The primary aspect that significantly decreases plastic waste in the micro injection moulding process is that it is associated with the production of small-sized goods and consumes less raw material. Shorter runner systems, for example, assist to reduce waste when compared to traditional injection molding.
Especially, micro injection molding is significantly important in the medical and healthcare industries, where extreme accuracy and cleanliness are crucial. Micro injection molding is widely utilized in the manufacture of medical equipment including drug delivery devices, catheters, diagnostic systems, optical and hearing aid components, and is especially useful for tools used in minimally invasive procedures like neurosurgery, aortic procedures, and so forth. Furthermore, new types of microfluidic devices are becoming increasingly popular and broadly useful in a variety of medical applications, including Point-Of-Care applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, medical sectors account for around a quarter of the global market share of micro injection molding.
Micro injection molding is also applied widely in other industries, including electronic and automotive industries. Micro injection molding is becoming more essential in the manufacture of microsystems since it is the most cost-effective technology for mass producing polymer micro-components.
Innovations and Sustainability
Micro over-moulding
 The technique of joining two or more moulded plastic or elastomer elements to create a single completed product is known as over-molding. The materials might be similar or dissimilar, resulting in a mechanical or chemical connection, which is different from insert molding, where a mechanical bond is normally formed. The first layer is known as the substrate, and it is covered by the second substance, known as the over-mould. Typically, the covering materials are thermoplastics or elastomers.
The technique of joining two or more moulded plastic or elastomer elements to create a single completed product is known as over-molding. The materials might be similar or dissimilar, resulting in a mechanical or chemical connection, which is different from insert molding, where a mechanical bond is normally formed. The first layer is known as the substrate, and it is covered by the second substance, known as the over-mould. Typically, the covering materials are thermoplastics or elastomers.
As over-molding does not require any outside materials such as adhesives, it is possible to obtain improved part functionality, which is important in medical devices, such as producing a water-resistant seal. Customers can benefit from precision over-molding for their medical device components by enhancing shot-to-shot uniformity and overall part quality. In addition, the robotics and automation of the technology enable low-cost high-volume production, and significantly reduce expensive and time-consuming assembly activities that potentially result in failures.
Optical micro molding
Micro-optic components are distinguished not only by their size, but also by their flatness, with surface relief feature depths of diffractive optical elements (DOEs) ranging from a few hundred nanometers to a few micrometres, in particular, relief depths of less than 100 microns are usual for refractive microlens arrays. Flatness qualities like this have paved the way for the utilization of production processes like injection molding, which offer considerable cost savings as component volume grows.
Not only is the resin less costly than glass, but the cycle time necessary to precisely mould a polymer optic is substantially less than the cycle time required to grind and polish an optic. Furthermore, multi-cavity molds may frequently be built to create more than one lens throughout each molding cycle, hence being ideal for projects that demand high numbers of components with commercial tolerances.
However, the use of injection molding for micro-optic manufacturing necessitates the optimization of design, mastering, tooling and production procedures, implying that tight collaboration between manufacturer and product developer is essential.

Towards nano injection molding
With the advanced technology, the injection molding industry is working on the level of sub-micron (≤ 10-6 m) and nanometre scales (≤10^-7m), which would be highly applicable in the field of medical diagnostics. Through the capacity to mold sub-miron features, nano injection molding offers new product innovation in consumer wearable and medical diagnostics devices. However, due to its influence on heat transfer and local flow fields, surface roughness greatly affects the replication of micro/nano features.
Depending on its dimension and aspect ratio, applications of nano injection molded features are highly valuable in hydrophobic functionality for the automotive industry, biomedical plastic cellware, light guide panel, microfluidics, lap-on-a-chip and medical diagnostic instruments, anti reflective panel for optics and display technology, optical grating, DNA sequencing chip for medical technology and others.
There are many other innovative breakthroughs in the field of micro injection molding for a more sustainable future. An example is the new sensors which are small and easy to install, taking up little room in the mold and could monitor temperature, pressure, warpage, shrinkage, and other processes. Another example is CNC machine tools and micro sinker EDM, as molders may use these devices to inject shots weighing less than 1 gram with minimum harm and good shot precision, and the advanced shrinking pressure and temperature sensors facility provide greater process control and real-time monitoring. Additionally, runnerless or reduced flow route molds are intended to conserve expensive materials while also allowing machine makers to redesign to achieve high precision and ultra-small shot sizes. Non-standard material designs, enhanced decreased wall thickness filling possibilities, stress reduction and mold annealing, and improved mold and material monitoring systems are among the latest developments.
Check out our 2022 CSR Report here.
References:
Micro injection molding market size, share, growth & forecast 2029 (no date) Adroit Market Research. Available at: https://www.adroitmarketresearch.com/industry-reports/micro-injection-molding-market#:~:text=Micro%2Dinjection%20Molding%20costs%20around,faster%20and%20less%20expensive%20machining. (Accessed: 26 May 2023).

Micro Systems, based in Golbourne, Greater Manchester, UK, has been a leading supplier for micro molding, mold design, mold manufacture and metrology, for major OEMs in the medical, pharmaceutical, ophthalmic, packaging markets and many more. Our innovative micro injection molding technology and equipment provides optimum precision and manufacture of all components to your specifications. For more information, please Contact us or visit our website.